Introduction to Wearable Tech in Healthcare
Wearable technology, commonly referred to as wearable tech, has rapidly evolved over the past decade, emerging as a transformative force within the healthcare sector. This category of technology includes devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and health-monitoring sensors that are designed to be worn on the body. These devices not only serve as tools for personal fitness but also play a critical role in the collection and analysis of health data. As the healthcare landscape continues to shift towards a more patient-centric model, the integration of wearable tech is proving to be invaluable in promoting proactive health management, facilitating remote patient monitoring, and enhancing the overall patient experience. The impact of wearable technology on healthcare extends far beyond simple fitness tracking; it is reshaping how healthcare providers deliver services and how patients manage their health.
The Rise of Wearable Technology
The rise of wearable technology can be traced back to the increasing consumer demand for devices that promote health and well-being. From the early days of pedometers to the sophisticated smartwatches available today, wearable tech has transitioned from niche gadgets to essential tools for health management. The surge in popularity can be attributed to several factors, including advancements in technology, the growing awareness of health issues, and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. For instance, devices such as the Fitbit and Apple Watch not only track physical activity but also monitor heart rates, sleep patterns, and even blood oxygen levels. This capability allows users to gain insights into their health in real time, making it easier to take preventive measures and seek medical advice when necessary.
In addition, the global pandemic has accelerated the adoption of wearable tech. With healthcare systems overwhelmed and in-person visits limited, patients turned to technology to monitor their health from home. Wearables offered a solution by allowing for continuous health monitoring and providing valuable data that healthcare professionals could use to make informed decisions about treatment plans. As a result, the pandemic has highlighted the importance of having accessible, real-time health information and paved the way for the integration of wearable tech into mainstream healthcare.
How Wearable Tech Enhances Patient Monitoring
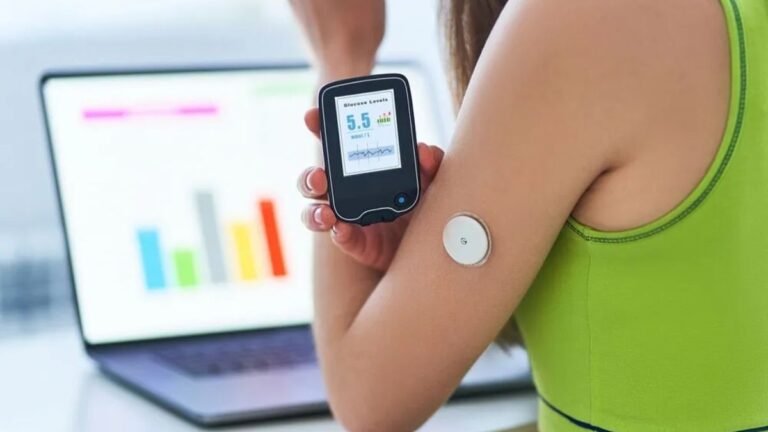
One of the most significant contributions of wearable tech to healthcare is its ability to enhance patient monitoring. Traditional patient monitoring often relies on in-clinic visits and manual data collection, which can be cumbersome and inefficient. In contrast, wearable devices provide continuous data collection, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health remotely. For example, devices like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) allow diabetic patients to track their blood sugar levels in real time, sending alerts when levels fall outside the desired range. This not only empowers patients to manage their conditions more effectively but also reduces the risk of complications that arise from uncontrolled diabetes.
Additionally, wearable tech can be particularly beneficial for elderly patients or those with chronic illnesses who require regular monitoring. Devices equipped with heart rate monitors, ECG capabilities, and fall detection features can alert caregivers and medical professionals to potential issues before they escalate. This real-time data allows for timely interventions, which can significantly improve patient outcomes. For example, if a patient’s heart rate exceeds a certain threshold, healthcare providers can be alerted immediately, allowing them to take action even before the patient experiences any symptoms.
Moreover, the ability to collect and analyze large amounts of health data from wearables leads to more personalized treatment plans. Healthcare providers can use this data to identify trends, understand patients’ behaviors, and tailor interventions accordingly. This shift from a reactive to a proactive approach in healthcare management can lead to better patient outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system.
The Role of Wearable Tech in Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions, are significant contributors to healthcare costs and morbidity worldwide. Wearable tech offers innovative solutions for managing these conditions, allowing patients to take a more active role in their health. For instance, patients with hypertension can use smartwatches that monitor their blood pressure throughout the day, providing them with insights into how their lifestyle choices affect their readings. This continuous monitoring empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health, such as adjusting their diet or medication in consultation with their healthcare providers.
In the realm of mental health, wearable devices are also making a difference. Devices that track sleep patterns and stress levels can help individuals identify triggers for anxiety and depression, providing valuable data for both patients and therapists. For example, the Oura Ring monitors sleep quality, heart rate variability, and activity levels, offering insights that can lead to improved mental well-being. By leveraging data from wearables, healthcare providers can develop comprehensive treatment plans that consider not just the physical but also the psychological aspects of chronic disease management.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Despite the numerous benefits of wearable tech in healthcare, concerns about data privacy and security remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption. As wearable devices collect sensitive health information, ensuring that this data is protected from unauthorized access is paramount. Patients must trust that their data will be used responsibly and kept confidential. The recent rise in data breaches across various sectors has raised alarms about the vulnerability of health data collected by wearables.
Healthcare providers and manufacturers of wearable tech must prioritize security measures to safeguard patient information. Implementing robust encryption methods, adhering to data protection regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and ensuring transparent data usage policies are essential steps in building trust with patients. Furthermore, educating patients about how their data will be used and the measures in place to protect it can enhance confidence in wearable technology.
Future Trends in Wearable Tech and Healthcare
The future of wearable technology in healthcare looks promising, with continuous advancements expected to further enhance its capabilities. One trend that is gaining traction is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms in wearable devices. These technologies can analyze health data more comprehensively, identifying patterns and predicting potential health issues before they occur. For instance, AI can help detect early signs of conditions such as atrial fibrillation, enabling timely interventions and reducing the risk of serious complications.
Another trend is the expansion of wearable tech into specialized fields such as telemedicine and remote patient care. As healthcare becomes increasingly decentralized, wearables will play a crucial role in facilitating virtual consultations and remote monitoring. Patients will be able to share real-time health data with their healthcare providers, enabling more informed discussions and decisions during telehealth appointments. This synergy between wearable tech and telemedicine will further enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery, especially in rural or underserved areas.
Moreover, as the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, we can expect greater interoperability among wearable devices and other healthcare technologies. This interconnectedness will allow for a more comprehensive view of a patient’s health, enabling providers to create holistic treatment plans that consider all aspects of a patient’s lifestyle and medical history.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wearable technology is revolutionizing healthcare by providing innovative solutions for patient monitoring, chronic disease management, and personalized treatment plans. As the adoption of wearable devices increases, so does the potential for improved health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system. However, addressing concerns regarding data privacy and security will be critical in fostering trust among patients and encouraging widespread acceptance. With ongoing advancements in technology and a focus on patient-centered care, the future of wearable tech in healthcare is bright, offering the promise of a healthier, more proactive approach to health management. The journey of wearable technology in healthcare is just beginning, and its impact is likely to grow as we embrace a more interconnected and data-driven healthcare ecosystem.